9.4.1 Description of the course
The course familiarizes students with the concepts and implementation of operating systems in computers. The course has been updated to include design thinking principles. Students are challenged to resolve operating systems challenges related to the Linux® operating system.
9.4.2 Description of participants
This is a mandatory course in the 4th semester of undergraduate studies at the Department of Management Informatics and Communication of Kathmandu University. A total of 37 undergraduate students enrolled in the Business and Information Systems program attended the course in the fall 2023 semester.
9.4.3 Description of gamified design thinking activities
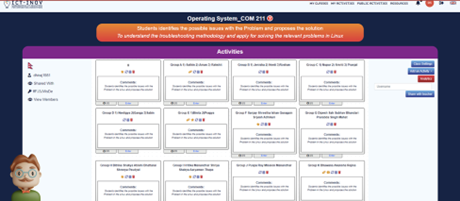
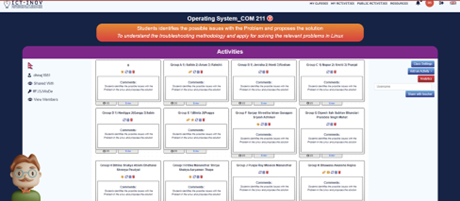
The ICT-INOV learning methodology based on design thinking was deployed in the course. Specifically, a learning activity was customized and integrated into the ICT-INOV digital learning platform. The primary objective of integrating the concept of design thinking was to challenge students work in groups to achieve a common goal. Students were asked to troubleshoot issues related to the Linux® operating systems. They were allowed to access the design thinking platform developed in the project. Students were divided into groups of 2 to 3 individuals. Some of the troubleshooting problems assigned to students are as follows:
- The system boots up, but the screen resolution is very low, while it was previously correctly set.
- A user is unable to log-in to a system they have previously logged-in to.
- An administrator needs to make changes to the home directory for all future new users.
- The system reports that a service has failed to start.
The ICT-INOV educational platform provides instructors with flexibility in structuring the learning activities based on well-accepted design thinking steps. Project activities in the context of the course were organized as follows:
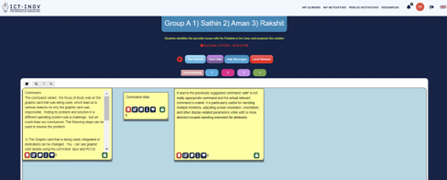
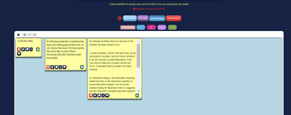
Step 1. Researching the problem.
Students were asked to identify the possible causes of operating system issues through thorough research. At this stage, students worked independently.
Step 2. Group findings.
Students discussed within their team the findings of their research, collectively identifying root causes of operating system issues.
Step 3. Solution synthesis.
Students identified potential solutions to operating system issues studied.
Step 4. Presentations.
Students presented their solutions to the class.