Description of the course
The course aims to develop knowledge of concepts of Computer Architecture as well as Computer Organization and design. The course addresses designing basic computers, central processing units, control units, input and output organization, and memory organization. Prerequisites of the course are Digital logic and Microprocessors. In the context of project ICT-INOV the course has been updated to include design thinking principles. Students deploy design thinking to implement the internal architecture of a computer system based on group work.
Description of the participants
The course is mandatory in the 3rd year of undergraduate studies at the Department of Mathematics of Kathmandu University. The ICT-INOV gamified design thinking methodology was deployed in July 2022. A total of 22 undergraduate students from the Department of Mathematics engaged in the activities.
Description of gamified design thinking activities
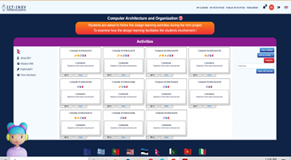
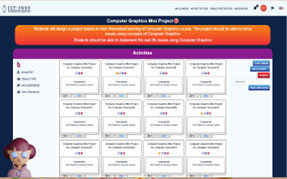
A learning activity was designed for the course following the paradigm of design thinking. The primary objective of integrating design thinking was to make the students work in a group to achieve a common goal. The students were asked to design a computer system based on the theoretical knowledge that they had gained through lectures and practical classes The students were encouraged to access the physical lab developed through the ICT-INOV project and use the digital learning platform for collaboration. They worked in groups of 1 to 2 individuals. The ICT-INOV educational platform provided instructors with flexibility in structuring the learning activities based on well-accepted design thinking steps.
Step 1: Team building.
Students were asked to form groups. As the class is comprised by 22 students, each group included of maximum 2 students, while one group included 3 students. After forming teams students were asked to introduce a group name and to design a group logo. A total of 11 groups were formed.
Step 2: Understanding the problem and identifying the solution.
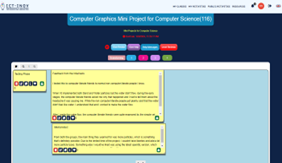
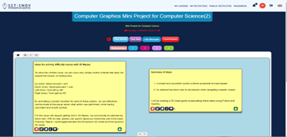
Students were asked to perform research towards understanding the problem in more detail. Students created lists of the issues that needed to be addressed while solving the problem and posted them on the ICT-INOV digital learning platform.
Step 3: Brainstorming for possible solutions and selecting the best solution based on consensus.
Upon developing a deeper understanding of the problem, students engaged in a brainstorming session discussing possible solutions. The outcome of this session was multiple potential solutions for addressing their identified problem. After listing the possible solutions students engaged in rigorous discussions with their team members to identify the most promising solution, namely one that was innovative and could be implemented with available resources.
Step 4: Identifying the list of hardware components necessary for solution design.
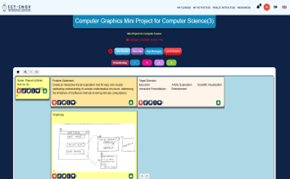
Students identified the list of equipment needed for designing the solution.
Step 5: Prototyping the system based on the identified solutions.
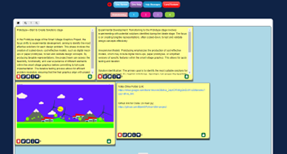
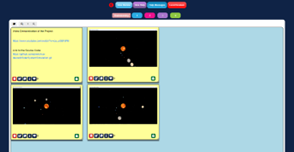
Students developed a prototype system using Nand to Tetris® software or paper.
Step 6: Presenting the solution.
Students presented the result of their work to faculty members.