Course description
The course constitutes an innovative training designed for educators who wish to enrich the learning experience of their students through the use of augmented reality.
Students have the opportunity to explore the potential of augmented reality. Through augmented reality educators actively involve students in class work and make complex concepts more accessible and interesting. The course is based on interactive and practical teaching approaches, which allow participants to acquire theoretical knowledge, but above all to put into practice the skills learned.
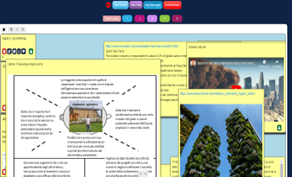
Students gain basic understanding of augmented reality apps, learning what it is and how it works, and they learn how to create augmented reality content using easily accessible tools and platform for presenting solutions. This approach helps stimulate student curiosity and interest, making learning an engaging and fun experience.
The integration of design thinking has enriched this training by making learning even more engaging and practical. It allowed students to take a holistic, needs-centered approach to augmented reality, ensuring that the proposed solutions are relevant, effective and engaging for the end audience.
Participants
The course has been created to be used in schools and universities with relevant profiles at various levels. The ICT-INOV methodology was deployed in the 2022 – 2023 academic year. Students aged 17 – 20 were engaged in the course managed by EUTrack. A total of 20 students attended the course.
Description of gamified design thinking activities
By using different techniques and direct observations that emphasize attitudes, behavior, and latent demands, design thinking was incorporated into the curriculum to assist students in developing a thorough contextual understanding of users. The goal of the design thinking implementation was to produce a more accurate needs analysis. The following steps were used to organize the activities.
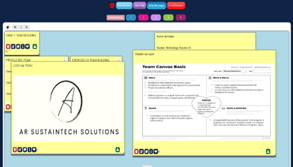
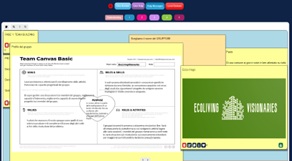
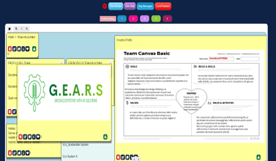
Step 1: Team building.
Students were split up into 4 teams of 5 members each. They were asked to select a team name and to describe the key elements of the group, such as their goals. To complete this work, they applied the team canvas template. The main purpose was to establish the team’s beliefs, working principles, roles, and goals in order to kick off the design thinking process.
Step 2: Understanding the problem and the users by creating an empathy map.
Students gathered information on users’ thoughts and feelings. This qualitative technique, in contrast to quantitative research, helped students comprehend user goals, objectives, pain areas, and more. This meticulous user study effort helped to obviate design mistakes throughout the implementation stage.
Additionally, students interviewed users to analyze their demands. A series of specific, predetermined questions of the type “how much” or “how many” were asked throughout the interviews, and the answers ranged from “yes” to “no,” “never,” “twice a week,” and other similar responses. The outcomes were deep insights into consumer emotions and thoughts. Students organized their unstructured material, which came in the form of notes, sketches, or photos, into an empathy map.
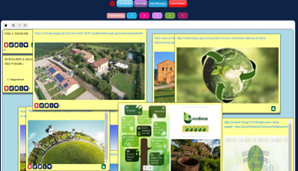
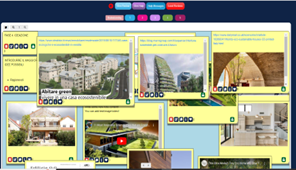
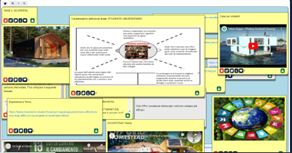
Students conducted research on the environmental and social challenges in urban environments and the demand for eco-sustainable housing for university communities. They interviewed other students to understand their housing needs, environmental behavior, and design preferences. In addition, they analyzed previous projects of eco-sustainable buildings to extract ideas, solutions and best practices applicable to the possible solutions.
Step 3: Problem define.
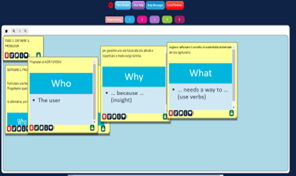
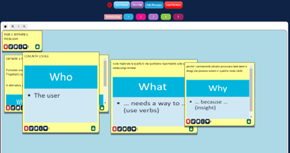
Students identified key challenges in university buildings, such as energy efficiency, waste management, use of sustainable materials, and integration of nature into the constructed environment. Students were asked to specifically identify the problem to be solved at the end of the design thinking process through precise definitions of “who”, “what” and “why” that help clarify the needs of the selected end users.
Step 4: Brainstorming and ideate.
Students worked in groups to generate creative ideas and innovative solutions to address the identified challenges. They introduced innovative design ideas integrated with sustainable technologies and efficient management practices.
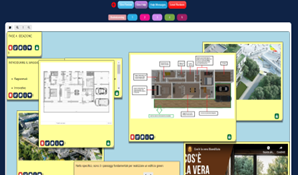
Step 5: Prototype and design.
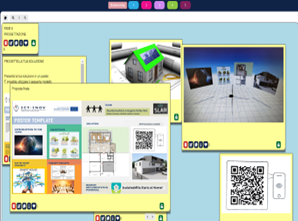
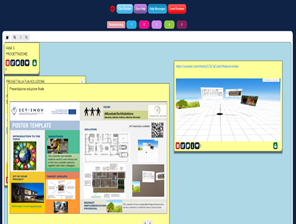
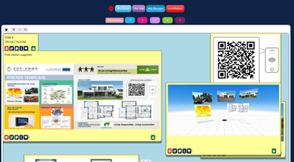
Students created prototypes of proposed solutions using poster templates to present an action plan that focused on developing a building project for an eco-sustainable apartment by integrating innovative ideas to reduce environmental impact and improve the quality of life of the occupants. Their solutions and products were presented by using the augmented reality application Eyejack Creator®.