Multimedia Learning Environment
Course description
The course aims to teach students to enhance their knowledge of using new technology by transforming their setting into a multimedia educational environment. The training aims to offer some easily applicable examples, such as virtual labs, virtual reality, serious games, digital storytelling, and robotics, to support and strengthen teaching and learning processes. Students are provided with adapted technological tools and methods to be used in and outside the classroom. The expected training activity has been structured to acquire know-how and develop the skills needed through theoretical deepening, simulation, and practical exercises. The course delivery is accompanied by the demonstration and an active participants’ co-involvement in the use of numerous technological instruments relevant to the topic as Oculus® Quest VR Platform, Oculus® Mixed Reality Capture, Chroma® Key, Samsung® Gear VR, Octagon® studio AR sets, Clevertouch® interactive touchscreen, LEAP® motion controller, and combination of the above instruments with Arduino® robotic artefacts.
Participants
The ICT-INOV methodology was deployed in the 2022 – 2023 academic year. Students aged between 22 – 30 were engaged in the course managed by EU-Track.
Description of gamified design thinking activities
Design thinking was integrated into the course to help students develop a deep contextual understanding of users via non-numerical means and direct observations that highlight attitudes, behavior, and latent needs. The purpose of design thinking deployment was to achieve a more effective needs analysis. Activities were organized in the following steps.
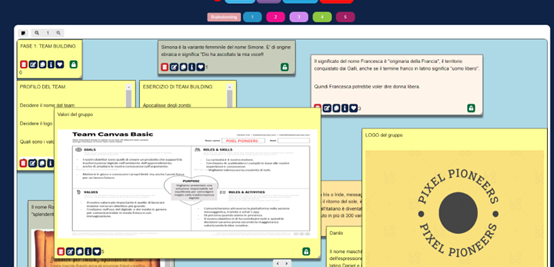
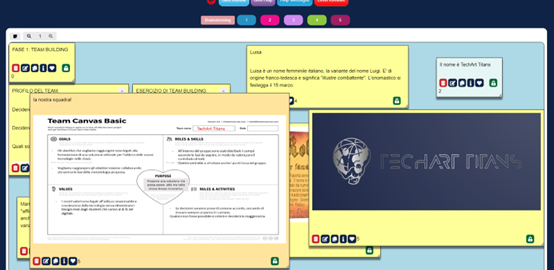
Step 1: Team building.
Students were split up into 4 teams of 5 members each. They were asked to select a team name and to describe the key elements of the group, such as their goals. To complete this work, they applied the team canvas template. The main purpose was to establish the team’s beliefs, working principles, roles, and goals in order to kick off the design thinking process.
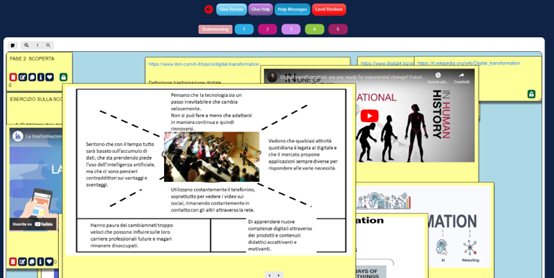
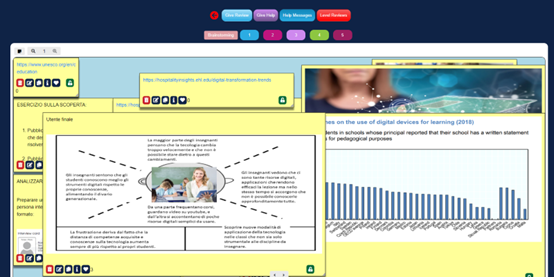
Step 2: Understanding the problem and the users by creating an empathy map.
Students gathered information on the assigned problem. In particular, they started to think about the motivations, hopes, needs, and pain of possible users. This process helped them to define the empathy map of the target group. The method provided deep insights. The students, that worked as designers, gained a better understanding of the problem issues.
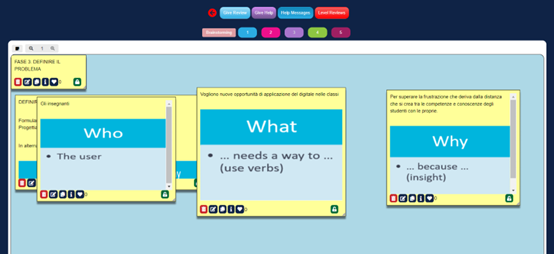
Step 3: Problem define.
After conducting research on the problem in focus, students were asked to specifically identify the problem to be solved at the end of the design thinking process through precise definitions of “who”, “what”, and “why” that help clarify the needs of end users.
Step 4: Brainstorming and ideate.
Students suggested ideas, from the most realistic ones to be implemented to the most impossible to realize. This part of the design thinking method allowed students to generate freely and develop innovative ideas by combining the work conducted in teams.
Step 5: Prototype and design.
Students built prototypes of their proposed solution in the form of a poster that they used to deliver a final presentation.