Course description
This is a hands-on and interdisciplinary training course that aims to empower students to tackle the challenge of transforming their campus into an eco-friendly and sustainable environment. By combining various aspects of robotics, multimedia resources, musical instruments, and design thinking students embark on an exciting journey to create an inspiring and environmentally conscious campus.
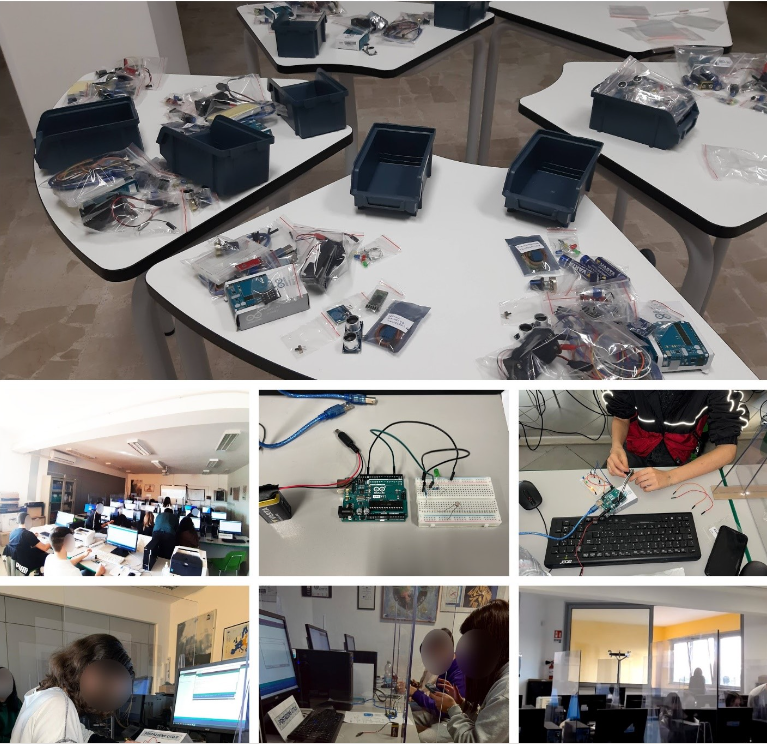
During the course, students delve into the world of educational robotics, learning to program robots and with Arduino®-based systems. They further leverage multimedia resources, such as video, audio, and augmented reality, to enhance their understanding and showcase their innovative solutions. The course is based on interactive and practical teaching approaches, which allow participants to acquire theoretical knowledge, but above all to put into practice the skills learned.
Through the design thinking approach, students develop a human-centered perspective and cultivate empathy as they identify and understand the needs of their school community. Through the use of ICT-INOV platform they employ design thinking principles to craft eco-friendly solutions. Working in teams, students hone their collaboration skills, combining the strengths of diverse perspectives to devise comprehensive solutions. Critical thinking is encouraged as they address complex challenges and evaluate the effectiveness of their ideas.
The ICT-INOV methodology and tools are integrated into this training to in-depth engage students in robotics, mainly in using the Arduino® platform. In this context, design thinking helps students identify the best solutions for the problem scenario suggested in the ICT-INOV digital learning platform.
Participants
The course has been created for use in schools and universities in STEM learning activities. The ICT-INOV methodology was deployed in academic year 2022 – 2023. Students aged 17 – 20 years have been engaged in the course managed by EUTrack. A total of 20 students participated in the course.
Description of gamified design thinking activities
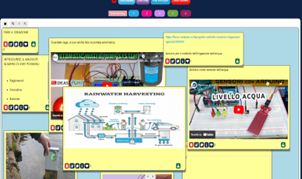
Students explored the intersection of eco-sustainability and robotics. Through hands-on activities, they leveraged robotics as a powerful instrument to address environmental challenges and develop sustainable campus solutions. With a focus on creativity and problem-solving, students used robotics to experiment, prototype, and optimize eco-friendly designs, fostering a greener and more environmentally conscious campus. This exciting combination of eco-sustainability and robotics empowered students to create meaningful and impactful changes for a sustainable future. Activities were organized in the following steps.
Step 1: Team building.
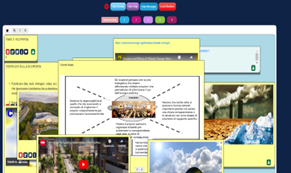
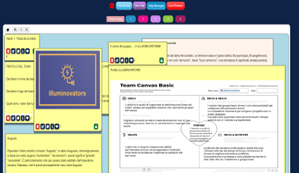
Students were divided into 4 groups of 5 members each. They were asked to select a team name and logo, which help generate a team identity. They decided on the rules of team collaboration and documented them into a team canvas, a useful tool to build the team, distribute the roles, know the members’ skills, and set a unique vision for the final objective.
Step 2: Understanding the problem and the users by creating an empathy map.
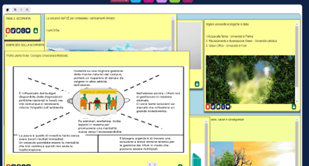
Students collected information about their thoughts and feelings through peer-to-peer and expert interviews. Social investigation techniques and tools were used at this stage to help students understand deeply the problem to be solved.
In addition, students researched articles on natural resources management. During this research, they identified the end-user profile and determined the possible challenges and opportunities through unstructured material in the form of notes, sketches, or photos. Finally, they constructed an empathy map regarding the user to be considered.
Step 3: Problem define.
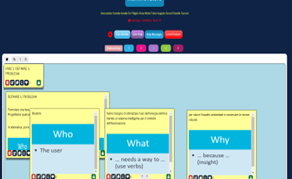
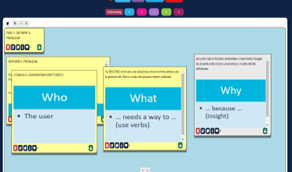
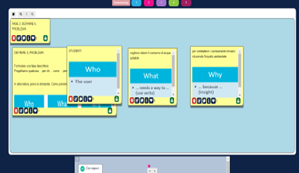
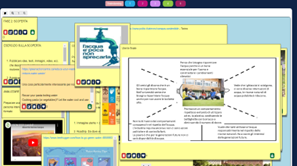
Students identified critical issues on natural resources management in a university campus and tried to define a specific problem to be solved based on their priorities and needs listed. They defined the problem using a clause of the form “who”, “what”, and “why” which allowed a clear description of user needs.
Step 4: Brainstorming and ideate.
Students worked in groups coming up with original solutions to problems. They introduced innovative design concepts, eco-friendly technologies, and effective management techniques.
Step 5: Prototype and design.
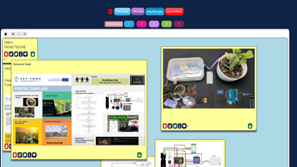
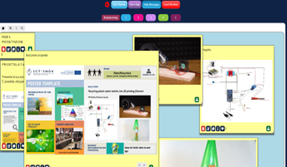
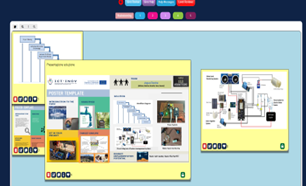
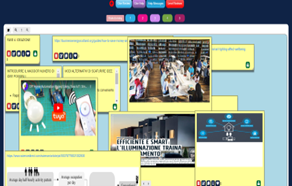
To finalize the design thinking process, students prepared their prototype by integrating Arduino® in their solution and drew a poster using the provided template to present their solution.